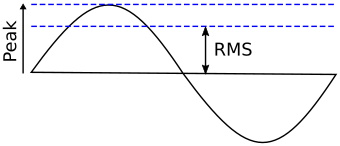
Because the value of an AC signal is continuously varying, it would be difficult to use formulas such as ohms law. In the specific case of a sine wave, the Root Mean Square (RMS) of the wave is used instead.
For alternating electric current, the RMS value is equal to the value of the constant direct current that would produce the same power dissipation in a resistive load. The average of a sine wave would produce a lower value.
If the waveform is a pure sine wave, the relationships between peak amplitude and RMS is RMS = peak * .707 and peak = RMS * 1.414.
More Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics Information:
• Mathematics Factoring Basics
• Direct Current
• Inductors in Series and Parallel
• How to Find the Andromeda Galaxy
• Capacitors
• How to Observe Constellations
• Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET)
• How to Learn Algebra
• Phase shift in AC Circuits
• Algebraic Order of Operations

