Built-in Utilities for Network Troubleshooting
By Stephen Bucaro
One of the most important responsibilities of a network administrator is to
fix any problems that arise with the network. This requires the ability to
troubleshoot the network. Conveniently, most operating systems come with
built-in utilities that can be used in the troubleshooting process. Described
below are the standard and most useful of these utilities.
Ping (Packet Internet Groper)
Ping is used to test the ability of two hosts on a network to communicate.
To test the connection, type in ping followed by the name or IP address
of the other host. If the host can be reached, ping will report the time required
to receive a reply from the host. If the host cannot be reached, ping will provide
a report containing some information that may indicate the cause of the problem.
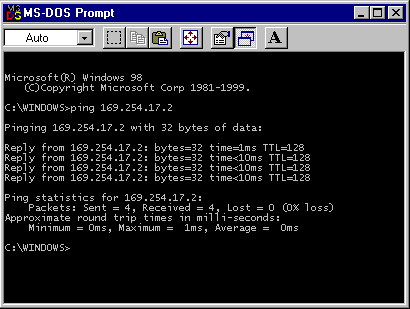
Windows computers will transmit four ping messages. If the host cannot be
reached, some operating systems will continue to send packets until to cancel the
ping command by pressing the [Ctrl][C] key combination.
Tracert (Trace Route) (Windows OS) / traceroute (Linux OS)
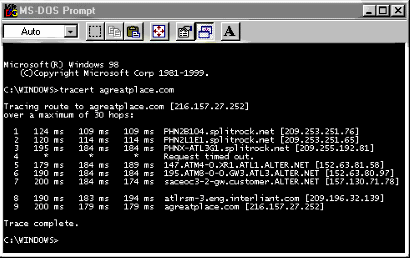
Tracert is used to trace the route between two hosts on a network. To trace a route,
type in tracert followed by the name or IP address of the other host.
Tracert will list each router it encountered along the path between a computer and
the destination host. It also reports the number of hops and the transit intervals
between routers going between a computer and the destination.
Ipconfig (Internet Protocol Configuration) (Windows OS) / ifconfig (Linux OS)
When dynamic configuration is used, the IP address of a host can frequently change.
Ipconfig is used to show the TCP/IP configuration of a computer.
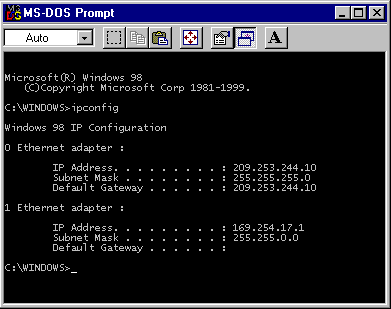
Shown above is an example of results returned by the ipconfig command.
It current TCP/IP network configuration values and refreshes Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) settings. Used without parameters,
ipconfig displays the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway for all adapters.
| 
