Network Cabling Design
By Stephen Bucaro
With a small network of a few work stations that is not expected to grow, you might
get away with just "winging" the cable installation, but the installation of a serious
computer network needs a plan. without a plan your network will be prone to frequent
failures and will be difficult to expand.
When designing your network, it's important to make sure your cabling system can
accommodate growth and the higher speeds of new technologies. A structured cabling
system is based on backbone cables that carry signals between floors, and horizontal
cables that bring signals to the work areas.
industry standards
A network installed without regard for industry standards will also be prone to
frequent failures and will be difficult to expand. The official standard for network
cabling is the TIA/EIA-568-A Commercial Building Telecommunications Cabling Standard.
The TIA (Telecommunications Industry Association) and the EIA (Electronic Industries
Association) are both members of ANSI (American Standards Institute).
• Before the TIA/EIA standards each vendor created incompatible cables and
connectors and the only resources for cabling guidance was proprietary documentation.
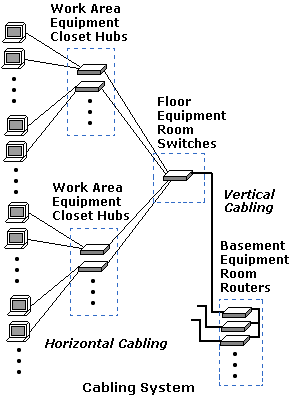
The cabling system specified in the TIA/EIA-568 standard is based on the star topology.
It specifies that the cables that service a work area on a floor should terminate
in a secure wiring closet which houses the hubs for the work area. Each floor
should have a secure equipment room which houses the network switches that connect
the floors horizontal cabling to the backbone cabling system.
Each building should have a secure main equipment room which connects to
the building backbone and houses the primary network equipment, for example routers,
gateways, and telecimunications equipment, and provides a location for connection to
the campus and public network.

The horizontal cabling might consist of Category 5 Unshielded twisted-pair
(UTP) cable. Category 5 UTP contains four-wire pairs with transmission characteristics
that support a bandwidth of 100 MHz and is capable of supporting 100 Mbps of Ethernet
data in a 100Base-T network. A cable segment may have a maximum length of 100 meters
(328 feet).
The vertical or Backbone cabling, used to provide connections between
equipment rooms on the floors of a building, might consist of multiple multimode fiber
optic cables that each support a bandwidth of up to 2 GHz in a 100Base-FX network.
Fiber optic cable may have a maximum segment length of 2 km or more.
| 
