Display Variable's value in Text in a Java Program
By Stephen Bucaro
In computer programming, a letter or digit is called a character and a collection of letters
or digits that make a phrase, sentence, or paragraph, is called a string. Java uses the
concatenate operator (+) to paste two or more strings together. However, you can also use the
concatenate operator to display the value of a variable with a String. Shown below is the Java code
to display the value of a variable with a String.
import javax.swing.*;
public class varsInText
{
public static void main(String s[])
{
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(300,300);
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
frame.setTitle("Variables in Text");
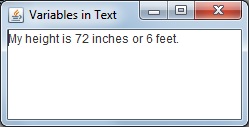
int inches = 72;
int feet = 6;
String tall = "My height is " + inches + " inches or " + feet + " feet.";
JTextArea myText = new JTextArea();
myText.setLineWrap(true);
myText.append(tall);
frame.add(myText);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
In the code shown above two integer variables are declared, one named inches is initialized with the value
72, and one named feet is initialized with the value 6. The line below that declares a String named
tall is initialized with substrings and the variables names. Java will automatically convert the integer
values to Strings for display.
Note that, although in Java, the names of primitive variable types, like int and char
begin with lower-case letters, the String variable type is capitalized. That's because strings
are actually objects, which makes them very powerful because they contain methods like
.length() and getChars.
I generally hate it when people add a bunch of extra code to an example. It confuses things.
But in this case I've included the javax.swing library and added code to create a
JFrame and a JTextArea. If I didn't add this extra code, you would need to use
the System.out.print command to output text, and I don't think that's an interesting
or realistic way to learn Java programming.
| 
