Display Text in a Java Program
By Stephen Bucaro
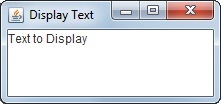
In computer programming, a letter or digit is called a character and a collection of
letters or digits that make a phrase, sentence, or paragraph, is called a string.
Example code to display a string in java is shown below.
import javax.swing.*;
public class displayText
{
public static void main(String s[])
{
JFrame frame = new JFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(300,300);
frame.setLocationRelativeTo(null);
frame.setTitle("Display Text");
JTextArea myText = new JTextArea("Text to Display");
myText.setLineWrap(true);
frame.add(myText);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Now I generally hate it when people add a bunch of extra code to an example. It confuses things.
But in this case I've included the javax.swing library and added code to create a
JFrame and a JTextArea. If I didn't add this extra code, you would need to use
the System.out.print command to output text, and I don't think that's an interesting
or realistic way to learn Java programming. The important part of this code is the line:
JTextArea myText = new JTextArea("Text to Display");
Which is the line that is responsible for the actual display of the text. You can modify the
code to display your own text by editing the text "Text to Display". Note that in Java and
other programming languages, a string is contained within double quotation marks.
If you wanted to experiment further, you could leave the JTextArea initializer empty
and instead declare a String variable, initialize it with your text, and then use the
JTextArea.append method to display the text in the program window, as shown below.
String myName = "Jim Shoe";
JTextArea myText = new JTextArea();
myText.append(myName);
Note that, although in Java, the names of primitive variable types, like int and char
begin with lower-case letters, the String variable type is capitalized. That's because strings
are actually objects, which makes them very powerful because they contain methods like
.length() and getChars.
If you're a beginner, for this example, I recommend downloading and installing the Java Development Kit from
Oracle's web site.
Type the code into a text file using a basic text editor like Window's Notepad (Do not use a word processor
because they insert formatting codes into the file), saving the file with the .java file extension. Then
use a batch file to compile the program. The batch file needs to contain the path to the compiler and the
path to the source file, an example of compile.bat is shown below.
c:\Program Files\java\jdk1.8.0_121\bin\javac c:\Users\Stephen\Desktop\program_name.java
pause
The pause command on the second line will cause the DOS shell to stay open until you press any key,
allowing you to read any errors. If successful, the compiler will create an executable file with the
.class file extension. Then use a batch file to run the program. The batch file needs to contain
the start command, the name of the java program launcher, and the name of the compiled java class
file (without the .class extension). An example of run.bat is shown below.
start javaw program_name
The javaw launcher displays the result of your program, or error information if it fails, in a window.
| 
