Motherboard Form Factors
By Stephen Bucaro
The form factor of a motherboard defines its dimensions. You need to make sure
that the computer case that you purchase can accommodate the form factor of the motherboard
that you select. It is also wise to select a motherboard with a commonly available form
factor in case you need to replace it.
The original IBM PC used over a hundred discrete digital circuit chips, so the
motherboard was very large. With greater integration, IBM was able to reduce the size
of the motherboard and released the AT (Advanced technology) form factor. The AT
motherboard was still quite large. Further integration resulted in the release of
the "Baby AT" form factor.
The "Baby AT" form factor was quite popular, but it was designed when keyboard, mouse,
I/O, and video circuitry where contained on circuit boards that where plugged into
"expansion slots" on the motherboard. Manufacturers wanted to put this circuitry
"on-board" to the motherboard to save cost.
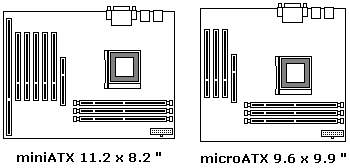
In 1995 the ATX form factor was designed to define standard locations for the keyboard,
mouse, I/O, and video connectors to allow for on-board circuitry. The continuing
increased integration of electronics allowed for smaller motherboards, so the Micro
ATX form factor was defined.
Smaller computers use less materials and are cheaper to manufacture. Smaller computers
also cost less to warehouse and to ship. Consumers like smaller computers too, because
they take up less space on the desk top. Manufacturers where able to shrink the size
of the case by putting the expansion slots on a separate circuit board, called a "riser
card", that plugs into the motherboard.
Motherboards Designed for Riser Boards
A Riser Board is a circuit board that connects at right angle to the motherboard
and provides additional expansion card slots. The LPX and Mini LPX form factors where
designed for the riser board configuration. The rider board plugs into a riser card
slot on the motherboard.
The NLX is an even smaller form factor designed to accommodate a riser board. The
NLX form factor has edge pins that plug into a connector on a riser board. The ATX and
microATX may also have a riser board that plugs into one of the PCI slots on the motherboard.
| 
