Ransomware is malware that works by encrypting files on your computer and requiring you have a password to decrypt them so that you can access them. To acquire the password you need to pay the criminal a ransom. You will be required to pay in an untraceable cryptocurrency such as bitcoin.
The best defense against ransomware is, of course, performing frequent backups. But for some organizations, the down time required to restore their systems costs more than the ransom, so they pay anyway. Paying a ransom encourages the criminal to move on the next victim.
Controlled folder access is a setting in Windows Security that blocks unauthorized or unsafe apps from making changes to files on your computer. To check your Controlled folder access setting, in the Start menu choose Settings (the gear icon) and scroll down to and select Update & Security. In the window that appears click on Windows Security (the shield icon).
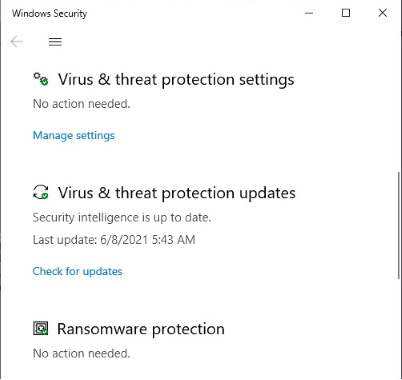
In the Windows Security Window that appears, select Virus & threat protection. In the Virus & threat protection window that appears, scroll down to Ransomware protection and click on Manage ransomware protection. In the ransomware protection dialog box that appears, check the switch below Controlled folder access. If it is set to No, click on it.
If the User Account Control warning box appears, click on the [Yes] button. That should dismiss the warning and set the switch to On. Below the switch, click on the "Protected folders" link to see a list of protected folders. You can unprotect a folder by clicking on its link and then on its associated [Remove] button.
Occasionally, an app that is actually safe will be identified as harmful. This happens because Microsoft wants to err on the side of caution. However, you can add an app to the list of safe or allowed apps to prevent them from being blocked.

