Windows 7 has several startup modes, called "Advanced Boot Options" that can help when troubleshooting the system. For example, the Safe Mode option lets you start the operating system in a limited state with only basic configuration settings and basic default device drivers. Other options start Windows with features intended for use by repair technicians or system administrators.
To access these alternate startup modes, you need to press the [F8] key while the computer is starting up, immediately after the BIOS startup messages, and before the Windows logo appears. It's a mater of timming, (I actually just keep tapping the [F8] key while the computer is starting until the Advanced Boot Options screen appears).
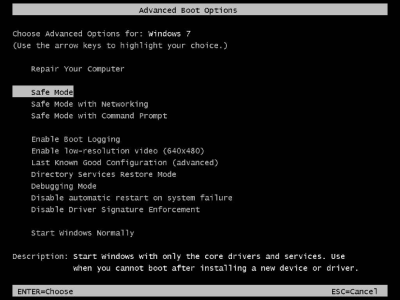
The Advanced Boot Options menu will display as shown above. Use the up or down arrow keys to highlight the selection of your choice, and then press the [Enter] key.
Safe Mode bypasses most startup configuration files, including most of the registry. It starts windows without most of the drivers. It loads only generic mouse and keyboard drivers and the default VGA driver (Vga.sys) which uses 640 x 480 resolution in 16 colors.
Safe mode lets you work with "bare bones" Windows. You have access to your drives, so you can copy or delete files. You can use System Restore to take your computer back to a restore point where it worked. You can use the Registry Editor to inspect or edit the Registry. Or you can use Device Manager to roll back a device driver that may be causing the problem.
Safe Mode with Networking is the same as Safe Mode, except it loads network drivers and network services that allow you to access the local network or the Internet to get help or download files.
Safe Mode with Command Prompt Starts Windows in safe mode with a command prompt window instead of the usual graphical Windows interface. This allows a repair technician or system administrator to run DOS commands to troubleshoot and repair the system. You can, for example, type C:\Windows\System32\rstrui.exe to start System Restore from a command prompt window.
Enable Boot Logging mode causes Windows to attempt to start normally, but to log its startup activity in a file named ntbootlog.txt stored in the %SYSTEMROOT% directory (normally C:\Windows). You can then reboot to Safe Mode and open the log file in Windows Notepad or DOS Edit and search for a line that contains the word "failure".
If Windows freezes before completing startup, the last line in ntbootlog.txt might provide a clue as to the cause of the problem. You may find that one or more steps fail during the startup process. Don't assume those are the cause of your current problem. Those steps may have been failing all along and you didn't know it.
Enable low-resolution video mode starts Windows using your current video driver with low resolution and low refresh rate settings. You can use this mode to reset your display settings or to troubleshoot video display problems.
Last Known Good Configuration. Every time Windows shuts down successfully, it stores a backup copy of the registry. Last Known Good Configuration uses the most recent backup copy of the registry to start your computer.
Directory Services Restore Mode Starts a Windows domain controller running Active Directory so that the directory service can be restored. This option is intended for network administrators.
Debugging Mode Starts Windows in an advanced troubleshooting mode. This option is generally used by the operating system's developer's or application programmers.
Disable automatic restart on system failure Windows is configured by default to automatically restart after is crashes (maybe you won't notice that it crashed). You can't do much to fix Windows if it's stuck in a loop where it fails, attempts to restart, and fails again repeatedly. This mode prevents Windows from automatically restarting if an error causes Windows to fail.
Disable Driver Signature Enforcement A driver is a very critical piece of software that works between the operating system and the hardware. In the past, poorly written drivers have caused problems in Windows. For that reason, Microsoft places a digital signature in any driver that they have tested and approved. Windows is configured by default to NOT start with unsigned drivers. However, just because a driver is unapproved by Microsoft, doesn't mean it will not work. Disable Driver Signature Enforcement mode allows Windows to load unsigned drivers.
Start Windows Normally allows you to get out of the startup menu and resume starting Windows normally in case you pressed the [F8] key accidentally.
What can you do in safe mode to troubleshoot your computer?
• You can use System Restore (Start | All Programs | Accessories | System Tools) to take your computer back to a previous point in time where it worked properly.
• You can use Control Panel (Start | Control Panel) utilities to change settings.
• You can use Device Manager (Start | Control Panel | System and Security | System) to disable, rollback, or update device drivers and configure hardware installed on your computer.
• You can open the System Information utility (Start | All Programs | Accessories | System Tools) to view details about your computer's hardware configuration, components, and drivers.
•You can open Event Viewer (Start | Control Panel | System and Security | Administrative Tools) to view a detailed log of system and program events that occurred on your computer.
•You can use the Registry Editor In the Start menu select Search, in the Search box type regedit and press [ENTER]. Making changes to Windows registry files is more for PC technicians and system administrators.
•You can open a Command Prompt (Start | All Programs | Accessories), which allows you to use DOS commands. Using DOS commands is for more for PC technicians and system administrators.
•You can use Windows Notepad (C:\Windows\notepad.exe) to view the boot log file ntbootlog.txt. if you previously started the computer in Enable Boot Logging mode.
If Windows fails to start or freezes up or the display becomes unintelligible, you can use one of the alternate startup modes, called "Advanced Boot Options" to help when troubleshooting the system.
More Windows Troubleshooting Articles:
• Free Firewall - ZoneAlarm
• How To Troubleshoot Your Computer Hardware
• What's With All Those Error Messages?
• CD-ROM Problems
• Windows 7 Startup Modes for Troubleshooting
• Fixing a Broken Laptop Screen Yourself is Easier Than You Think
• Create Recovery Discs for Windows Vista with HP Recovery Manager
• How to Troubleshoot, Dissemble, and Repair a Laptop Display
• Free Open Source CPU Temperature Monitor
• The Windows Recovery Console

