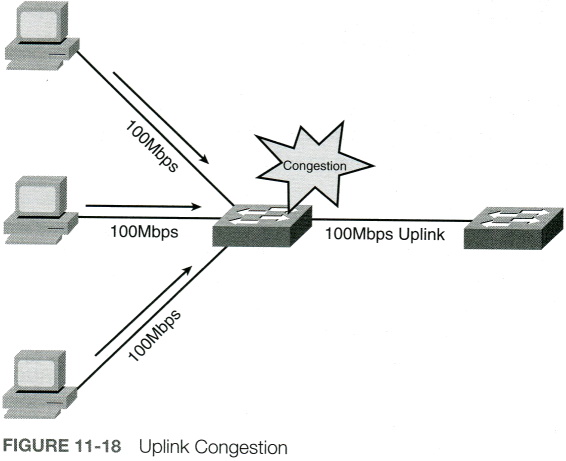
If all ports on a switch are operating at the same speed (for example, 1Gbps), the ports most likely to experience congestion are ports connecting to another switch or router. For example, imagine a wiring closet switch connected (via Fast Ethernet ports) to multiple PCs. That wiring closet switch has an uplink to the main switch for a building. Because this uplink port aggregates multiple 100Mbps connections and the uplink port is also operating at 100Mbps, it can quickly become congested if multiple PCs are transmitting traffic that needs to be sent over that uplink, as shown in Figure 11-18.
To help alleviate congested links between switches, you can (on some) switch models logically combine multiple physical connections into a single logical connection over which traffic can be sent. This feature, which is illustrated in Figure 11-19, is called Link aggregation.

Although vender-propiettary solutions for link aggregation have existed for some time, some solutions faced a couple of common issues:
• Each link in the logical bundle was a potential single point of failure.
• Each end of the logical bundle had to be manually configured.
In 2000, the IEEE ratified the 802.3ad standard for link aggregation. This standard supports Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP). Unlike some of the older vender-proprietary solutions, LACp supports automatic configuration and prevents an individual link from becoming a single point of failure. Specifically, with LACP, if a link fails, that link's trafic is forwarded over a different link.
The Cisco Systems implementation of LACP is called EtherChannel. Groups of interfaces that make up an EtherChannel bundle are often referred to as a Link aggregation group (LAG). An EtherChannel group can be configured to act as a Layer 2 access port and support only a single VLAN, or it can be configured to act as a Layer 2 802.IQ trunk and support multiple VLANs of the LAG.
A LAG can also be configured as a Layer 3 routed interface if the switch supports that feature. In the case of a Layer 3 Ethernet Channel, an IP address would be applied to the logical interface that represents the LAG.
Another term related to LACP and LAGs is port bonding, which also refers to the same concept of grouping multiple ports and using them as a single logical interface.
About The Author
Anthony Sequeira, CCIE No. 15626, is a Cisco Certified Systems Instructor (CCSI) and author regarding all levels and tracks of Cisco Certification. Anthony formally began his career in the information technology industry in 1994 with IBM in Tampa, Florida. He quickly formed his own computer consultancy, Computer Solutions, and then discovered his true passion-teaching and writing about Microsoft and Cisco technologies. Anthony joined Mastering Computers in 1996 and lectured to massive audiences around the world about the latest in computer technologies. Mastering Computers became the revolutionary online training company, KnowledgeNet, and Anthony trained there for many years. Anthony is currently pursuing his second CCIE in the area of Security and is a full-time instructor for the next-generation of KnowledgeNet, StormWind.com. Anthony is also a VMware Certified Professional.
CompTIA Network+ N10-008 Cert Guide contains proven study features that allow you to succeed on the exam the first time. Expert instructor Anthony Sequeira shares preparation hints and test-taking tips, helping you identify areas of weakness and improve both your conceptual knowledge and hands-on skills, essential for successful completion of the performance-based testing items on the exam. This complete, CompTIA-approved study package includes the following:
• A test-preparation routine proven to help you pass the exams
• Clearly defined chapter learning objectives covering all N10-008 exam topics
• Chapter-ending review questions and exam preparation exercises, which help you drill on key concepts you must know thoroughly
• The powerful Pearson Test Prep practice test software, complete with hundreds of well-reviewed, exam-realistic questions, customization options, and detailed performance reports
• 40 performance-based exercises to help you prepare for the hands-on exam questions
• A free copy of the CompTIA Network+ N10-008 Simulator Lite software, complete with meaningful lab exercises that enhance your hands-on skills
• More than 60 minutes of video mentoring
• A final preparation chapter that guides you through tools and resources to help you craft your review and test taking strategies
• An Exam Essentials appendix that quickly recaps all major chapter topics for easy reference, both in print and interactive digital format
• A key terms Glossary in both print and on the companion website, which acts as an interactive flash-card application
• Study plan suggestions and templates to help you organize and optimize your study time
• A 10% exam discount voucher (a $33+ value!)
Well regarded for its level of detail, study plans, assessment features, challenging review questions and exercises, video instruction, and hands-on labs, this approved study guide helps you master the concepts and techniques that ensure your exam success.
Master the topics on the CompTIA Network+ N10-008 exam, including:
• Network topologies and media types
• IP addressing
• Network services
• Data center architectures and cloud concepts
• Routing, Ethernet switching, and wireless networking
• Network availability and disaster recovery
• Network security
• Remote access
• Network troubleshooting
Reader Paulo Cardoso says, "This is a great book. In addition, it comes with great additional resources."
Learn more about the CompTIA Network+ N10-008 Cert Guide at amazon.com
More Networking Protocols and Standards:
• Unicast, Multicast, Broadcast. What Does It Mean?
• Evolution of the Microsoft NOS (Active Directory)
• Network Operating Systems
• Network Switches
• What Is Fabric Networking?
• IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol (NDP)
• A Simple Description of the IPv6 Header and Datagram
• An Introduction to the Types of VPNs
• Integration of IPv6 with IPv4
• TCP/IP Utilities



