RADIUS Protocol
By Stephen Bucaro
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) is an application layer protocol
that provides centralized Authorization, Authentication, and Accounting management for
users who connect and use a network service. These networks may incorporate modems,
access points, DSL, VPNs, etc.
Radius server is usually a background process running on a UNIX or Microsoft Windows server.
The NAS (Network Access Server) forwards remote access requests to a RADIUS server
via the RADIUS protocol. A request includes access credentials (username and password).
Communication between a NAS and a RADIUS server are based on UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
a connectionless service. RADIUS protocols include CHAP, PEAP, PAP, EAP, or SIP Digest.
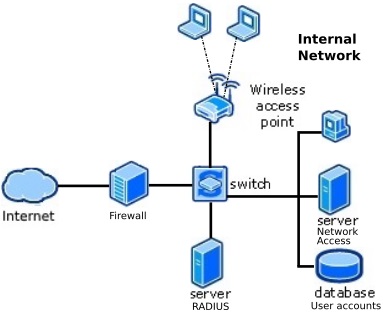
When the RADIUS server receives the Access-Request from the NAS, it searches a database
for the username and password provided. The RADIUS server does not contain a database,
it is a protocol that defines how to work with a central database that maintains user
profiles that all remote access servers share to provide authentication and authorization services.
RADIUS server can communicates with a domain controller for user authentication.
If the username does not exist in the database or domain controller, either a default
profile is provided or the RADIUS server sends an Access-Reject message which may be
accompanied by a message indicating the reason for the refusal. After successful
user authentication, remote access policies defined on the RADIUS server are applied
to the connection.
The accounting features of the RADIUS protocol can be used independently of RADIUS
authentication or authorization. The RADIUS accounting functions track when a session
starts and stops, the amount of resources (such as time and data) used during the session.
More Networking Protocols and Standards:
• Network Cabling and Components
• Internet Protocol versions IPv4, IPv5 and IPv6
• The OSI Application Layer
• Active Directory : How Objects Are Stored and Identified
• RADIUS Protocol
• Network Operating Systems
• Network Gateways
• Free eBook: IPv6 Addressing
• Evolution of the Microsoft NOS (Active Directory)
• Ports and Sockets
| 
