Set the box-sizing Property
By Stephen Bucaro
When using box elements, e.g. div, to lay out a webpage or website template,
it's important to understand how the dimensions of the box are defined.
Back when Internet Explorer controlled 90% of the browser market Microsoft
defined the dimensions of a box element as shown below.
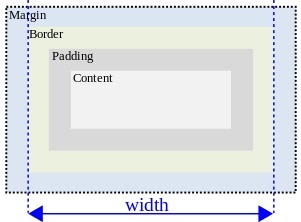
Internet Explorer box model
Microsoft defined the width and height of a box element as the distance
between the outer edges of the box's border. This makes logical sense to me.
But with webpage rendering rules varying wildly between different competing
companies browsers, in 1994 an international consortium of companies got together
to form the W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) with the purpose of creating
standards for web page elements and how their properties were defined.
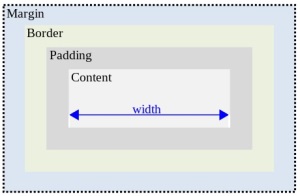
W3C box model
The W3C defined the width and height of a box element as the distance between
the outer edges of the box's content. This makes no sense to me.
The CSS box-sizing property lets you change the way box element sizes
are defined.
| Value | Description |
| border-box | The width and height are the distance between the outer edges of the box's border |
| content-box | The width and height are the distance between the outer edges of the box's content |
| initial | How width and height are defined determined by browser |
| inherit | How width and height are defined inherits from its parent element |
Shown below is a default div without the box-sizing property, where the width and height refer to box's content.
<div style="width:200px; height:80px; padding:20px; border:1px solid black;">Div without box-sizing property</div>
Div without box-sizing property
| 
