Context selectors
By HTML Tutorials
When creating a web page it is often required to put one tag into another. In order
to use these tags correctly, use selectors, which work only in the certain context.
For example, defining the style for tag <B> only when it is located in the
paragraph <P>. The Contextual selector consists of simple selectors which are
separated with space.
Syntax:
Tag1 Tag2 { ... }
In this case style will be applied to the Tag2, when it is located in the Tag1, as it
is shown below.
<Tag1>
<Tag2> ... </Tag>
</Tag1>
The usage of contextual selectors is shown in the example 9.1.
Example 9.1. Contextual selectors.
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=windows-1251">
<title>Contextual selectors</title>
<style type="text/css">
P B {
font-family: Times, serif; /* Font family */
font-weight: bold; /* heavy faced type*/
color: navy; /* blue colour of the text */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div><b>heavy faced type</b></div>
<p><b>The heavy faced type of the text and text highlighting takes part simultaneously</b></p>
</body>
</html>
In this example we see the common use of the tag <B> and its use, when
it is put into paragraph <P>. The color of the text and font are changed,
as it is shown in the figure 9.1.
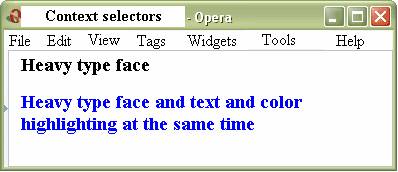
Figure 9.1. Design of the text, depends on the nesting of tags.
Note: It is not obligatory that context selectors consist of only one embedded tag.
Depending on the situation it is supposed to apply one and more than one tags, logically
embedded into each other. When using classes and identifiers, contextual selectors give more
capacities. It allows defining the style only for that element, which is located in the
certain class, as it is shown in the example.
| 
