Port forwarding is a function of the NAT (Network Address Translation) protocol. It redirects a communication request from one address and port number connection to another while the packets are traversing a network gateway, such as a router. This technique is used to hide hosts residing on an internal network from hosts on external networks outside of the gateway. It does this by remapping the destination IP address and port number of the communication to an internal host.
In a home network, hosts obtain Internet access through a DSL or cable modem connected to a router configured with NAT. The NAT device's external interface is configured with a public IP address. Hosts on the home network communicate only with a private IP address. Computers behind the switch or router are not visible to hosts on the Internet.
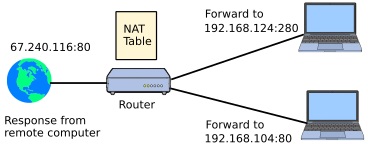
NAT translates between a public IP address and private IP addresses allowing multiple computers on your home network to appear to the internet as one computer with one address. When a computer inside your home network wants to connect to a computer on the internet, it sends a connection request to the router (the configured Default Gateway). The router takes that connection request (a SYN request) and changes the "reply-to" or return address from the private IP of the computer to the public IP of the router, so that the response from the host on the internet will be sent to the router. The router makes an entry in a database, called the NAT table, so that it remembers it later.
When the response comes back from the remote computer (a "SYN-ACK"), the router looks in its NAT table and sees a connection to the host on that port that was previously initiated by a computer on the private network, changes the destination address to the private address of the computer, and forwards it to that computer on the private network.
In this way, packets can continue to transit back and forth between the public Internet and your private network with the router transparently changing the addresses. When the connection is terminated, the router removes the entry from the NAT table.
More Networking Basics:
• Definition: Cloud Computing
• Turning Your Home into a Wi-Fi Network
• Network Cabling For Beginners
• Network Administrator Street Smarts: A Real World Guide to CompTIA Network+ Skills
• Fiber Optic Cabling For Beginners
• Cable Broadband Internet Service
• Workgroups and Domains
• Computer Networking Basics
• Network+ Certification Exam Tutorial - DHCP And RARP
• Comparing Different Cloud Architecture Types

