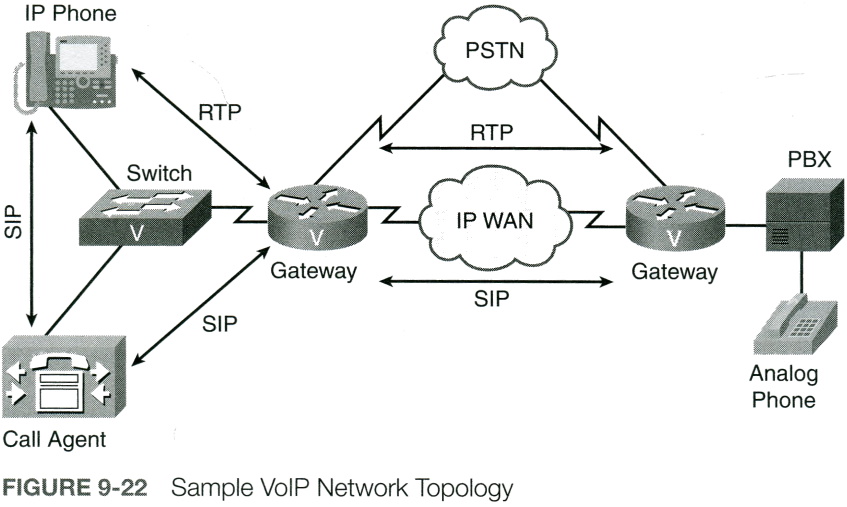
A voice over IP (VoIP) enabled network digitizes speech into packets and transmits those packets across a data network. This allows voice, data, and even video to share the same medium. In a network with unified communications (UC) such as voice, video and data, specialized UC servers, controllers, devices, and voice gateways are also likely to be used. In a cloud computing environment, they may be virtualized as well. Figure 9-22 shows a sample VoIP network topology. Not only can a VoIP network provide significant cost savings over a traditional PBX solution, may VoIP networks offer enhanced services (for example, integration with video conferencing applications and calendaring software to determine availability) not found in traditional corporate telephony environments.
IP phone
An IP phone is a telephone with an integrated Ethernet connection. Although users speak into a traditional analog handset (or headset) on the IP phone, the IP phone digitizes the user's speech, packetizes it, and sends it out over a data network (via the IP phone's Ethernet port).While an IP phone is a common example of a VoIP endpoint, an alternative is software running on a computer.
Call agent
A call agent is a repository for a VoIP network's dial plan. For example, when a user dials a number from an IP phone, the call agent analyzes the dialed digits and determines how to route the call toward the destination.
Gateway
A gateway in a VoIP network acts as a translator between two different telephony signaling environments. In figure 9-22, both gateways interconnect a VoIP network with the PSTN. Also, the gateway on the right interconnects a traditional PBX with a VoIP network.
PBX
A private branch exchange (PBX) is a privately owned telephone switch traditionally used in corporate telephone systems. Although a PBX is not typically considered a VoIP device, it connects into a VoIP network through a gateway, as shown in figure 9-22.
Analog phone
An analog phone is a traditional telephone, like the ones individuals used to have in their homes. Even though an analog phone is not typically considered a VoIP device, it can connect to a VoIP network via a VoIP adapter or, as shown in figure 9-22, via a PBX, which is connected to a VoIP network.
SIP
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a signaling, setup, and management protocol used with voice and video sessions over IP networks. SIP, in conjunction with other protocols, specifies the encoder/decoder (codec) that will be used for voice and video connections over the network.
RTP
Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) is a protocol that carries voice and interactive video. Notice in figure 9-22 that the bidirectional RTP stream does not flow through the call agent.
About The Author
Anthony Sequeira, CCIE No. 15626, is a Cisco Certified Systems Instructor (CCSI) and author regarding all levels and tracks of Cisco Certification. Anthony formally began his career in the information technology industry in 1994 with IBM in Tampa, Florida. He quickly formed his own computer consultancy, Computer Solutions, and then discovered his true passion-teaching and writing about Microsoft and Cisco technologies. Anthony joined Mastering Computers in 1996 and lectured to massive audiences around the world about the latest in computer technologies. Mastering Computers became the revolutionary online training company, KnowledgeNet, and Anthony trained there for many years. Anthony is currently pursuing his second CCIE in the area of Security and is a full-time instructor for the next-generation of KnowledgeNet, StormWind.com. Anthony is also a VMware Certified Professional.
CompTIA Network+ N10-008 Cert Guide contains proven study features that allow you to succeed on the exam the first time. Expert instructor Anthony Sequeira shares preparation hints and test-taking tips, helping you identify areas of weakness and improve both your conceptual knowledge and hands-on skills, essential for successful completion of the performance-based testing items on the exam. This complete, CompTIA-approved study package includes the following:
• A test-preparation routine proven to help you pass the exams
• Clearly defined chapter learning objectives covering all N10-008 exam topics
• Chapter-ending review questions and exam preparation exercises, which help you drill on key concepts you must know thoroughly
• The powerful Pearson Test Prep practice test software, complete with hundreds of well-reviewed, exam-realistic questions, customization options, and detailed performance reports
• 40 performance-based exercises to help you prepare for the hands-on exam questions
• A free copy of the CompTIA Network+ N10-008 Simulator Lite software, complete with meaningful lab exercises that enhance your hands-on skills
• More than 60 minutes of video mentoring
• A final preparation chapter that guides you through tools and resources to help you craft your review and test taking strategies
• An Exam Essentials appendix that quickly recaps all major chapter topics for easy reference, both in print and interactive digital format
• A key terms Glossary in both print and on the companion website, which acts as an interactive flash-card application
• Study plan suggestions and templates to help you organize and optimize your study time
• A 10% exam discount voucher (a $33+ value!)
Well regarded for its level of detail, study plans, assessment features, challenging review questions and exercises, video instruction, and hands-on labs, this approved study guide helps you master the concepts and techniques that ensure your exam success.
Master the topics on the CompTIA Network+ N10-008 exam, including:
• Network topologies and media types
• IP addressing
• Network services
• Data center architectures and cloud concepts
• Routing, Ethernet switching, and wireless networking
• Network availability and disaster recovery
• Network security
• Remote access
• Network troubleshooting
Learn more about the CompTIA Network+ N10-008 Cert Guide at amazon.com
More Networking Topologies Articles:
• Routers
• How Do Fiber Optic Couplers Work and How are They Made?
• The Difference Between a Broadcast Domain and a Collision Domain
• How to Choose the Proper Fiber Optic Connector for Your FTTH (Fiber To The Home) Installation
• The Complete Guide to Fiber Optic Connectors
• A Guide to Broadband Internet Connections
• Difference Between Unmanaged, Web Smart and Managed Switch
• The Secret of Maintaining Your Fiber Optic Network
• Understanding Basic Terms in Indoor Fiber Optic Cable Installation
• Network Interface Cards (NIC)



