Firewall Perimeter Network (DMZ)
By Stephen Bucaro
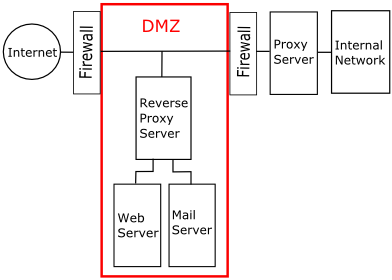
A DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) or Perimeter Network is the area between the firewall that
protects the network from untrusted external networks (the Internet) and the firewall
that protects the internal network. Intruder attacks on web servers and mail servers
are common. Having an additional firewall makes it more difficult for an intruder to
gain access to the organizations internal network.
Any service that is being provided to users on the external network can be placed in
the DMZ. Hosts in the internal network communicate with services in the DMZ through an
intervening firewall, this allows hosts in the DMZ to provide services to both the
internal and external network.
The most common services placed in the DMZ are:
• web servers
• mail servers
• FTP servers
• VoIP servers
If a web server needs to communicate with an internal database that may contain sensitive
information, it can communicate with internal database servers through an application firewall.
You can create a perimeter network with a single firewall, but this configuration is more
complicated to configure and is less secure.
To increase security, a reverse proxy server can be used to isolate the servers in the
DMZ from direct access by external networks. A reverse proxy server, like a proxy server,
is an intermediary, but is used the other way around. A proxy server hides internal host
addresses and only exposes its own address to outside clients. A reverse proxy server hides
outside clients addresses and only exposes its own address to internal hosts.
More Network Security Articles:
• Nessus Network Vulnerability Scanner
• Top Ways to Prevent Data Loss
• Intrusion Detection System (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
• How to Protect Your Business From a Cyber Attack
• Public Key Infrastructure
• What is Cross Site Scripting?
• Denial of Service Attack (DoS) Detection and Mitigation
• Domain Name System (DNS) Vulnerabilities
• What is a SQL Injection Attack?
• Essentials of Endpoint Device Backup
| 
