T-Carrier
By Stephen Bucaro
T-carrier is a time-division multiplexed (TDM) digital signal that has been used by the telephone
companies for many decades. The idea being that in order to communicate a voice signal, it is not
necessary to transport the entire analog signal, the wave is sampled at the relatively slow rate of
8000 samples per second, and then digitized into an 8 bit number.
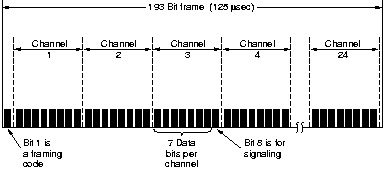
24 of these 8-bit signals (called a DSO) are time-division multiplexed into a 1.544 Mbps t-carrier
signal for transmission over telephone lines. At the other end of the line the 24 samples are
de-multiplexed and each 8-bit sample decoded to produce an analog level. With proper smoothing of the
signal, the original voice signal is re-created.
For voice communication, only 7-bits are used to code the signal, the 8th-bit being used to carry
signaling information (e.g. ready, ring, busy tone). For data communications the entire 8-bit signal is used.
Multiple T1 streams can be further multiplexed onto higher carriers. A T2 circuit is 4 T1 circuits
multiplexed, resulting in a transmission rate of 6.312 Mbps. A T3 circuit is 18 T1 circuits multiplexed,
resulting in a transmission rate of 44.736 Mbps. A T4 circuit is 168 T1 circuits multiplexed,
resulting in a transmission rate of 274.176 Mbps.
T1 streams can be multiplexed to provide networks with high-bandwidth, permanent WAN connections
between sites. If such a high-bandwidth is not needed, a customer does not need to purchase all
24 of the T1 DS0 circuits. A low cost option is to purchase only the number of circuits required,
called "fractional T1 service".
Although T1 was introduced in 1962, it was so efficient that a huge amount of it was installed.
And because of its reasonable cost and great flexibility, much of it is still in use today.
More Networking Protocols and Standards:
• Unicast, Multicast, Broadcast. What Does It Mean?
• IP version 6 (IPv6) Advantages and Implementation
• Networking Protocols, Ports, Standards, and Organizations What Does it All Mean?
• Integration of IPv6 with IPv4
• IEEE 802 Standards Specify the Basics of Physical and Logical Networking
• VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol)
• The OSI Data Link Layer
• IEEE 802.11 Wireless Modulation Methods
• Ports and Sockets
• Remote Control Protocols
| 
