Changing the Size of an Image on Your Webpage
By Stephen Bucaro
One of the most important procedures in designing a webpage is proper sizing of images.
There are two ways to resize an image. 1. Use a graphics application. 2. Set the width
and height attributes in the html img tag.
o Actually there is a third method: Set the img elements width and height properties
using CSS (Cascading Style Sheets). The advantage of doing it with CSS is that it
allows you to dynamically resize the image. This article, however, is about html.
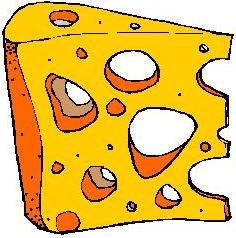
Actual Size Image 236 x 238 pixels
|

Image resized to
118 x 119 pixels
|
<img border="0" width="118" height="119" src="cheese.jpg" />
The easiest method is to Set the width and height attributes in the html
img tag, however this has a disadvantage. Using this method, the browser has to perform
the work of resizing every time the page loads, thus lengthening the page's load time.
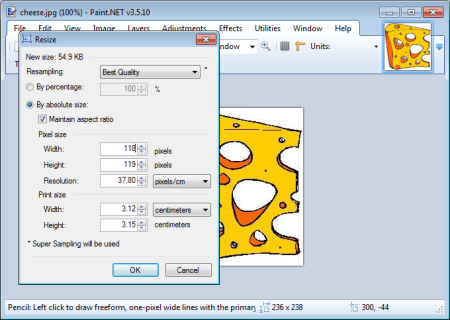
I recommend using a graphics application to resize the image, and then uploading the
resized image to your web site. The graphics application that I recommend is the free
Paint.Net application.
There are two important things to consider when resizing an image. 1. Maintaining
the aspect ratio. 2. Loss of resolution.
The aspect ratio is the ratio of the image's width to its height. If, when changing
an image's size you do not maintain the same aspect ratio, the image will appear
distorted. In a graphics application you can simply set a checkbox, configuring the
application to maintain the aspect ratio.

Aspect ratio not maintained
when resizing image.
But if you resize an image by setting the width and height attributes in the html
img tag, you'll need to perform a calculation to maintain the aspect ratio. For example,
if you double the width of the image, you must also double the height.
If you resize an image to a larger size, the graphics application or browser must
fill in missing data. The graphics application or browser can't guess what detail
to fill in, so an enlarged image will be blurry. In a graphics application might
be able to use the application's sharpen feature to recover some of the missing
detail, but this is only possible to a limited extent.
There is an image format that does not lose detail when you change its size. That
is the vector graphics format. A vector file does not contain pixel data, but instead
it contains instructions about how to draw the image. There are several different vector
file formats, not all compatible with all browsers, and because the browser must
draw the image, they slow page load time.
More HTML Code:
• HTML5 Input Type - URL
• Radio Button Basics
• Webpage DOCTYPE Declarations Explained
• HTML Definition List
• HTML noscript Tag
• HTML Select List Basics
• HTML center Tag
• Changing the Size of an Image on Your Webpage
• When to Use the nofollow Attribute value
• HTML5 Input Type - Email
| 
