Networking - Fiber Distributed Data Interface
By Stephen Bucaro
The Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI) standard was designed by the
American National Standards Institute (ANSI X3T9.5 standard ) in the mid-1980s,
and later turned over to the International Organization for Standardization
(ISO). The OSI specification for FDDI is not actually a single specification,
but a collection of four specifications for the the physical and media-access
portions of the OSI reference model.
FDDI uses pulses of light and fiber optic cable to send signals with a 100
Mbps throughput. It uses a token passing routine similar to Token Ring networks,
except that it uses two rings with signals flowing in opposite directions
(referred to as counter-rotating).
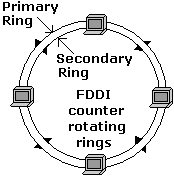
The purpose of the dual rings is to provide high reliability. The dual rings
consist of a primary ring and a secondary ring. During normal operation, the
primary ring is used for data transmission, while the secondary ring remains
idle. If the primary ring experience problems, the secondary ring will take over
data transmission.
FDDI can use two types of fiber optic cable, single-mode or
multimode. A mode is a variation in the intensity of the light in
the cable. basically, a mode can be thought of as a ray of light. Single-mode
fiber allows only one mode of light to propagate through the fiber. Multimode
cable allows multiple modes of light to propagate through the fiber.
Because multiple modes of light will arrive at the end of the fiber at different
times, a characteristic referred to as modal dispersion, the bandwidth
and distances that can be achieved using multimode fibers is limited. Because
only one mode of light is allowed to propagate through Single-mode fiber, modal
dispersion is not present. Single-mode fiber is capable of achieving higher
throughput over longer distances.
The number of modes that a fiber-optic cable exhibits depends on the dimensions
and variation of refractive indices of the core and cladding of the cable.
Multimode fiber systems use an LED as the light generating device, while single-
mode fiber systems use lasers.
Fiber optic media has several advantages over copper media. Because fiber optic
does not emit electrical signals, it cannot be tapped to permit unauthorized
access to the data being transmitted. Fiber optic is also immune to electrical
interference allowing it to support higher throughput than copper. For these
reasons FDDI is frequently used as a high speed backbone for large networks.
More Networking Topologies Articles:
• Frame Relay WAN Protocol
• What Are Fiber Optic Attenuators?
• The Difference Between a Broadcast Domain and a Collision Domain
• Access Points and Wireless LAN Controller
• Static Versus Dynamic Routing
• How to Set up a Private Network
• Network Broadcast Storms
• Difference Between Unmanaged, Web Smart and Managed Switch
• What is an Ethernet Switch?
• Wireless Networks
| 
