The Registry is the central database for everything about your computer. It stores configuration information about the operating system, hardware, software, and types of files on the computer.
The registry database consists of "keys" and "values". A key is a "place" to store a value. A key may store many values, or it may have subkeys, each which store values. The Windows 2000 registry has five top level keys as listed below.
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE | Hardware configurations |
| HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG | Operating system settings |
| HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT | Files types and software objects |
| HKEY_USERS | All users configurations |
| HKEY_CURRENT_USER | Currently logged in user configurations |
The Registry is normally modified through Administrative or Control Panel utilities, but it is possible to edit the Registry directly. Making an incorrect modification to the Registry can cause your computer to fail to start, so it's wise to backup the Registry before making any changes.
To backup the registry, you can export it to an ASCII file with the .reg extension. You can export the Whole Registry or just a branch of the Registry. First select or create a folder where you would like to save the exported registry. To export the Registry, open the Registry Editor program by selecting Start | Run and typing regedit in the Run dialog box.
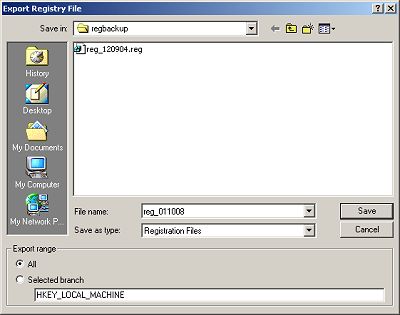
In the Registry Editor programs Registry menu, select Export Registry File... In The Export Registry File dialog box, navigate to the folder where you would like to save the exported registry. Then enter a name for the exported registry file (for example reg_date). Make sure the Save as type: drop down list has Registration Files selected. This will automatically add the .reg extension to the file. In the Export Range section, set the All radio button. Then click on the Save button.
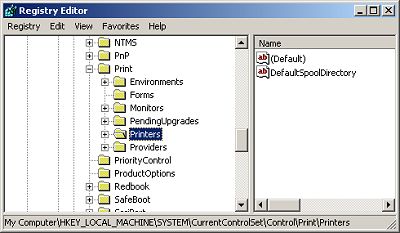
If you export the entire registry, the .reg file will be quite large, between 20MB and 30MB. You might want to export only a specific branch of the registry. To export a branch, highlight the branch in the left pane of the Registry before selecting Export Registry File... in the Registry Editor programs Registry menu. In the Export Range section, make sure the Selected branch radio button is set.
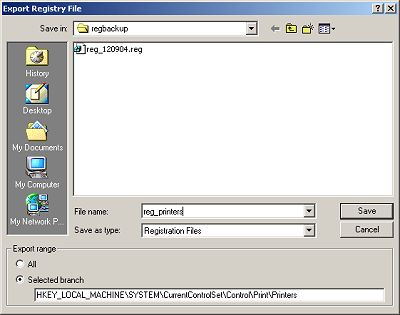
One reason to export a Registry file is to be able use a text editor to search it. The Registry Editor prgram has a Find... function in the Edit menu, but it's more difficult to use.
• Do not double-click the file to open it in a text editor, as the default action for a file with the .reg extension is to merge it back into the Registry.
• Before you edit the registry file, make a backup copy.
Right-click on the file and select Open with... in the popup menu, or drag and drop the file to Notepad or Wordpad. Then use the capabilities of the text editor to search and edit the exported registry branch.
After you have completed editing the file, you can import it back into the Registry by selecting Import Registry File in the Registry Editor program's Registry menu, or by double-clicking on the file name.
The Registry is normally modified through Administrative or Control Panel utilities, but by using the method described in this article it is possible to safely edit the Registry directly.
More Maintain and Upgrade Your PC Articles:
• Four Tips to Finding Quality PC Cleaner Software
• How To Properly Install A New Motherboard
• Printing Troubleshooting Guide
• Wireless Router Setup
• Partitioning Your Hard Disk
• Installing An Optical Drive Guide
• How Power Surges Can Smoke Your PC
• How To Refill Your Ink Cartridge
• How to Install a New DVD Drive
• Digital Photography Printing - Simplifying the Pixels and DPI's

