Cable broadband Internet service uses a coaxial cable and/or fiber-optic cable from the provider's office to your home or office. The provider may a have a distribution box near your location where they run a drop cable to your home or office. At your end, the coaxial cable connects to a router or modem. The router or modem connects to your network or computer through an USB cable, Ethernet cable, or wireless circuit.
Cable Internet service has a download speed of 2 Mbps to 50 Mbps or even faster. The upload speeds are usually much slower than the download speeds, ranging from 384 Kbps to 20 Mbps or faster.
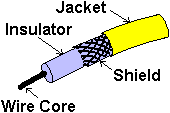
Coaxial Cable
One advantage of coaxial cable is that it has an outer metallic shield that protects the signal from external electromagnetic interference. This means it can be run next to other electronic devices without interference.
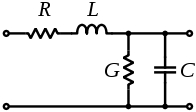
Schematic representation
of coaxial impedance
One disadvantage of coaxial cable is that it has losses caused by an electrical characteristic called impedance. Impedance is a combination of losses caused by resistance and losses caused by inductance and capacitance. Inductance is the tendency for the cable to act like a coil. Capacitance is the tendency for the cable to act like a capacitor. The longer the cable is, and the higher the signal frequency, the more the losses become. Another problem is that the end of a causes reflections.
Coaxial cable losses are reduced by impedance matching, which basically involves choosing the proper cable. With cable lengths of less than 750 feet, RG59 type cable can be used. RG11 type cable allows lengths of up to 1,500 ft. Signal reflections are reduced by having the proper value termination resistance.
More Networking Basics:
• Definition: Cloud Computing
• Satellite Broadband Internet Service
• Turning Your Home into a Wi-Fi Network
• Network Cabling For Beginners
• Best CompTIA Network+ Certification Exam Preparation Materials
• Virtualization For Dummies Cheat Sheet
• Cloud Delivery Models
• Synchronous, Asynchronous, Isochronous. What Does it Mean?
• A Complete Explanation of Cloud Computing
• What is the Internet of Things?

