To "harden" a server means to configure it in a way to enhance its security. One way to enhance a servers security is to configure it so that it runs only the services and protocols that are required for its role.
For example, a server being used as a web sever needs to run Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and Secure Sockets Layer Protocol (HTTPS). Other protocols such as Simple Mail Transport Protocol (SMPT) and Telnet should not be running.
If the Telnet is left running unnecessarily, a hacker may be able to connect to the server and launch an attack. If SMPT is left running unnecessarily, a hacker may be able to exploit vulnerabilities in that protocol to launch an attack.
Security Configuration Wizard (SCW)
One reason system administrators tend to leave unnecessary services running and unnecessary protocols installed is because it's difficult to identify which are necessary and which are not. The SCW, built into Windows Server can be used to analyze a system and guide you through the process of creating, editing, applying, or rolling back a security policy.
Start the SCW by selecting Start | Administrative Tools | Security Configuration Wizard. The SCW will guide you through several screens where you can create, edit, and apply security policies. The security policy that you create is an XML file that, when applied, configures services, network security, specific registry values, and audit policy. After you create the file, you can view it at:
c:\Windows\security\msscw\Policies\Text\test.xml
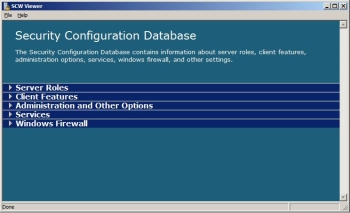
If you prefer to determine security settings yourself, rather than be guided by the SCW, the SCW provides an extensive database that you can browse to learn about the different security settings. It indicates security settings for various server roles, client features, administration options, service configurations, and firewall settings.
Keep the System Updated
Hackers are continuously probing servers searching for vulnerabilities that they can exploit. When Microsoft learns of a vulnerability that has been discovered by hackers, they provide patches and hotfixes to close the vulnerability. If the vulnerability is very serious, they release the patch or hotfix as quickly as possible. Patches for less serious problems will be released on the regularly scheduled second Tuesday of every month.
Many system administrators configure Automatic Update to install all updates as soon as they're released. However, sometimes an update designed to fix one problem creates another problem. By knowing that updates will be released on second Tuesday of every month, administrators can plan for, and manage their deployment.
Some system administrators use a special service like System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) or Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) which allows them to test the updates for compatibility with their systems and software and to selectively deploy only the updates that will not cause problems on their systems.
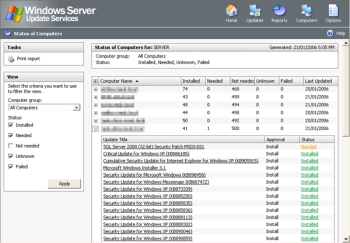
Both of these applications are available at Microsoft Download Center.
Use a Firewall
A firewall is software or hardware (or a combination of both) that control the traffic coming in and going out of a network or a computer. Controlling the traffic coming in to the network or computer blocks malware from being installed. Controlling the traffic coming in and going out of a network or a computer prevents hackers from acquiring critical security information.
Newer versions of the Windows operating system have a built-in firewall that is installed and enabled by default. Tests have shown that the Windows Firewall is as good as any in protecting a computer or a server. However, some system administrators prefer to install a third-party firewall such as ZoneAlarm or Comodo because they feel these companies have more experience and are more focused on security than Microsoft. They also may suspect that Windows Firewall gives Microsoft special privileges to probe their systems.
Use Antivirus Software
Hackers are continuously attempting to install malware on networks and systems. One type of malware is adware. Adware is advertising software which downloads and automatically displays advertisements on a computer. These advertisements are usually in the form of a pop-up window.
Another type of malware is spyware. Spyware is software secretly installed on a computer for the purpose of collecting information about computer's and users without their knowledge. Some spyware programs are key loggers designed to capture usernames and passwords.
The most insidious type malware is a virus. A Virus is software designed to cause damage to a computer system or it's data. The most defining property of a virus is it's ability to replicate itself and spread from one computer to another. In fact many virus do no damage. They do nothing more than replicate themselves and spread from one computer to another. However, the act of a virus replicating itself can reduce the performance of a computer or network.
An antivirus program is software which is designed to detect and remove virus threats before they have a chance to cause damage to the system. If an antivirus program finds a virus, it warns the user about the virus and prompts the user about how to deal with the virus.
One option to deal with a virus is to delete it. Another option is to quarantine the virus and forward it to the developer of the antivirus program before deleting the virus. Antivirus program developers use the information provided to update their virus definitions.
An antivirus program should be configured to provide real-time protection and to update its virus definitions automatically. There is a particularly insidious virus that disables a systems antivirus program before it begins its damage, therefore it's important to monitor the status of your antivirus program frequently.
Conclusion
By hardening a server, you're making it much more difficult for hacker to launch a successful attack against the system. One way to harden a server is to disable unnecessary services and remove unnecessary protocols. Other important methods of hardening a server are to use antivirus software, use a firewall, and keep the system updated with the latest patches and hotfixes.
More Windows Administration Information:
• What Are Windows Server Containers?
• How to Harden a Server
• Server Virtualization - What It's All About
• Three Important Techniques for Securing a Wireless Network
• How to Create a Bootable USB Drive
• How to Disable Windows Firewall in Windows 7
• How to Backup Mails and Address Book of Outlook Express
• How to Change Process Priorities in Windows Task Manager
• Disable Annoying 'Get Windows 10' Message
• Computer Technician's Guide to Dealing with Customers

