Core i3 is an entry-level 2-core processor using the 32nm Westmere micro-architecture.
Core i3 Features
• Integrated dual-channel DDR3 memory controller
• separate DMI interface to peripheral devices
• HD-capable graphics controller
• separate 256 KB L2 cache for each core
• Up to 4 MB L3 cache shared between 2 cores
• SSE4 instructions
• HyperThreading technology
• support for Virtualization
Because Core i3 is entry-level certain features are not supported.
Core i3 Features Not Supported
• Turbo Boost Technology,, which temporary increases frequency of one or more cores, is disabled
• Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) instructions are not supported
• Trusted Execution technology not supported
• VT-d virtualization not supported
Core i3 CPUs for budget desktop use are packaged in Socket 1156 Land-Grid Array (LGA) package. Core i3 CPUs for budget notebook and mobile use are packaged in BGA-1023 or 988 micro-PGA package.
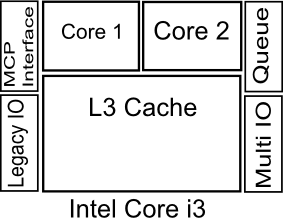
Core i3 Processors
| Processor | Clock Speed | Power Disipation |
| Core i3-530 | 2.93 GHz | 73 watts |
| Core i3-540 | 3.06 GHz | 73 watts |
| Core i3-550 | 3.2 GHz | 73 watts |
| Core i3-560 | 3.3 GHz | 73 watts |
| Core i3-2100 | 3.1 GHz | 65 watts |
| Core i3-2120 | 3.3 GHz | 65 watts |
Al Chartreux says, "I helped a friend put together a build with the Core i3-530. It's a nice machine, and we're pleased with how it came out and performs. Like all of Intel's desktop CPU's, the Core i3-530 is a quality chip, and at a price of $114.99, certainly among the most inexpensive of Intel's desktop offerings, which tend to be priced at a range of $150 to $300 for low to mid-range chips, and $310 and higher for high-end chips. At a Thermal Design Power (TDP) of 73 watts, the i3-530 is a cool-running chip that doesn't gobble down loads of electricity, so those looking for power-efficient, quiet machines will be happy with it. Click here for more information.
More Computer Architecture Articles:
• Monolithic Kernel vs Microkernel vs Hybrid Kernel
• Microcontroller Registers
• Electronic Circuits
• Operating System Memory Paging Hardware Support
• Intel's Core i7 Processors
• CPU Process Scheduling
• Load Balancing Multiple CPUs in Symmetric Multiprocessing
• Operating System Memory Paging - Page Table Structure
• The AMD Athlon 64 X2 Processor
• AMD's Microarchitectures


