The Celeron processor is a budget processor offering moderate performance at an affordable price. This processor is suitable for use in notebook and desktop computers running home-office applications and providing access to the Internet. It is not be recommended for use in a high performance game machine or a heavily accessed web server.
The Celeron D processor, released in December 2005, is based on the Prescott core. It runs at clock speeds up to 3.33 GHz, has a 533MHz Front Side Bus Speed, a 16kb L1 cache, and an integrated 256K L2 cache. Celeron D models 347 and higher use the 65nm Cedar Mill core and have a 12KB + 16KB (Data + Instructions) L1 Cache and a 512KB L2 cache.
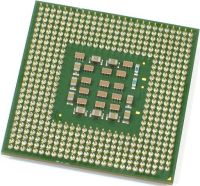
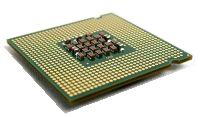
Pins on bottom of processor - Contact pads on bottom of processor
This processor uses either the socket 478 or the LGA775 Socket. The two socket types are not interchangeable because the newer 775-pin Land Grid Array has no pins on the processor. Gold contact pads provide the connection between the processor and the socket on the motherboard.
Some Celeron D models feature Intel's Extended Memory 64 Technology which allows them to access larger amounts of memory and support 64-bit extended operating systems. Some models, including those with J in their model number, feature the Execute Disable Bit (XDB), which prevents viruses from exploiting buffer overrun vulnerabilities.
Celeron D Processors
| Model | Process | L2 Cache | Clock Speed | EM64T | XDB |
| 310 | 90 nm | 256 KB | 2.13 GHz | ||
| 315 | 90 nm | 256 KB | 2.26 GHz | ||
| 320 | 90 nm | 256 KB | 2.40 GHz | ||
| 325 | 90 nm | 256 KB | 2.53 GHz | ||
| 325J | 90 nm | 256 KB | 2.53 GHz | X | |
| 326 | 90 nm | 256 KB | 2.53 GHz | X | X |
| 330 | 90 nm | 256 KB | 2.66 GHz | ||
| 330J | 90 nm | 256 KB | 2.66 GHz | X | |
| 331 | 90 nm | 256 KB | 2.66 GHz | X | X |
| 335 | 90 nm | 256 KB | 2.80 GHz | ||
| 335J | 90 nm | 256 KB | 2.80 GHz | X | |
| 336 | 90 nm | 256 KB | 2.80 GHz | X | X |
| 340 | 90 nm | 256 KB | 2.93 GHz | ||
| 340J | 90 nm | 256 KB | 2.93 GHz | X | |
| 341 | 90 nm | 256 KB | 2.93 GHz | X | X |
| 345 | 90 nm | 256 KB | 3.06 GHz | ||
| 345J | 90 nm | 256 KB | 3.06 GHz | X | |
| 346 | 90 nm | 256 KB | 3.06 GHz | X | X |
| 347 | 65 nm | 512 KB | 3.06 GHz | X | X |
| 350 | 90 nm | 256 KB | 3.20 GHz | ||
| 351 | 90 nm | 256 KB | 3.20 GHz | X | X |
| 352 | 65 nm | 512 KB | 3.20 GHz | X | X |
| 355 | 90 nm | 256 KB | 3.33 GHz | X | X |
| 356 | 65 nm | 512 KB | 3.33 GHz | X | X |
• Don't confuse the Celeron D with processors without the "D", which are based on the Northwood core and have only 8kb of L1 cache and a 128 KB L2 cache.
• Note that, unlike the Pentium D, the Celeron D is not a dual core processor.
More Computer Architecture Articles:
• Virtual Memory and Memory Paging
• Operating System File Management
• Processor Affinity in Symmetric Multiprocessing
• How Computer Chips are Made
• First-Come, First-Served CPU Scheduling Algorithm
• Computer Buses
• Digital to Analog Convertion with a Microcontroller
• Operating System Memory Allocation Methods
• Operating System Process Control Block
• Operating System Memory Paging

