Hibernation is a feature of Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI), found on some notebook computers that activates when you close the lid. Hibernate saves an image of your desktop with all open files and documents to a file on your hard drive and then powers down your computer. When you turn the PC's power on, your files and documents are restored on your desktop exactly as you left them.
There are two main problems with hibernation. First, if you search the Web for "PC hibernation", you'll find that it's one of the most problem plagued computer technologies ever created. Many PC's have a problem waking up from hibernation. That's because not all hardware and software are 100 percent ACPI compliant.
Second, hibernation takes up a lot of hard disk space. The hibernation image file (hiberfil.sys) can be equal in size to the amount of RAM you have installed in your PC. If you have a 4GB of RAM in your PC, you'll lose about 4GB of Hard disk space when hibernation is enabled.
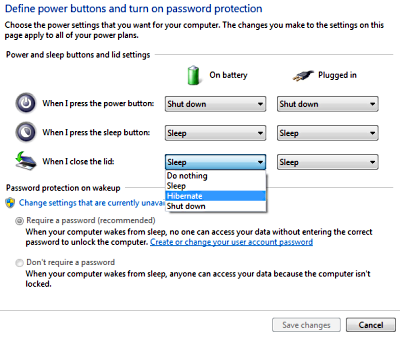
To disable hibernation, click on the System and Security group in Control Panel. In the System and Security window, click on Power Options. In the left panel of the Power Options window, click on "Choose what closing the lid does". In the various drop-down lists, select another choice besides "Hibernate". Then click on the [Save Settings] button.
Now you don't need to worry about hibernation errors and you've freed up a large amount of disk space.
More Windows Tips:
• How-to Capture the Computer?s Screen
• Display Multiple Clocks in Windows 7 Taskbar
• Disable Hibernation in Windows 7
• Stop Desktop Icons from Randomly Refreshing
• Configure the Start Menu
• VLC Free Open-Source Media Player
• Make the Insertion Point Cursor More Visible
• Add the Undo Button to File Explorer in Windows 10
• Use ReadyBoost to Improve PC performance
• Change the Windows 7 Desktop Background

