The Athlon 64 X2 is the first dual-core CPU manufactured by AMD. It is essentially two Athlon 64 cores on one die joined together with additional control logic. The cores share one dual-channel memory controller.

The benefit of dual-core processors is their ability to process more software threads at the same time, this is called thread-level parallelism (TLP). However, many programs are written with only one thread, and are therefore unable to utilize the processing power of the second core.
Athlon 64 X2's that use Socket 939 support dual channel DDR SDRAM memory; PC-3200 (DDR-400), PC-2700 (DDR-333), PC-2100 (DDR-266) or PC-1600 (DDR-200) SDRAM unbuffered DIMMs. They support HyperTransport up to 14.4GB/s.
Athlon 64 X2's that use Socket M2 support dual channel DDR2 SDRAM memory; PC2-6400 (DDR2-800), PC2-5300 (DDR2-667), PC2-4200 (DDR2-533) or PC2-3200 (DDR2-400) SDRAM unbuffered DIMMs. They support HyperTransport 20.8GB/s.
• Athlon 64 FX's use a 1,207-pin Socket F and have their multipliers unlocked for hardware hackers and gamers.
&bull DDR stands for "Double Data Rate" which means the memory can be accessed on both the rising and falling edges of the memory controller's clock cycles. DDR2 RAM uses an improved design that allows DDR2 RAM to use a lower voltage and operate at a higher speed than DDR memory.
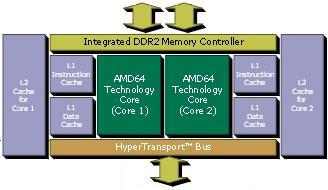
&bull HyperTransport is a connection method that transfers data faster. On a motherboard, the HyperTransport bus connects the PCI slots, AGP slots and USB ports to the CPU and memory and also provides a connection between the CPU and memory.
All Athlon 64 X2's have a 128KB L1 Cache (64KB for instructions and 64KB for data) and up to 1MB Level 2 cache per core. Depending upon the core and the clock speed, Athlon 64 X2's dissipate between 65 and 125 Watts of power.
Athlon 64 X2's support MMX, 3DNow!, SSE, SSE2, and SSE3. These are all extensions to the instruction set for enhanced multimedia. The first ones, "MMX" stands for MultiMedia eXtensions. 3DNow! is a set of 21 new instructions developed by AMD. SSE (Streaming SIMD Extensions) is a set of 70 new instructions, including Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD) floating-point, additional SIMD integer, and cacheability control instructions.
Athlon 64 X2s support the NX bit, a security feature used to prevent malicious software from inserting their code into another program's data storage area and running their own code. This is known as a buffer overflow attack.
Athlon 64 X2 Processor Models
Socket939
| Model | Clock | L2 Cache | Core | Power | Process |
| Athlon 64 X2 3800+ | 2.0 GHz | 1 MB | Manchester | 89.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 3800+ | 2.0 GHz | 1 MB | Toledo | 89.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 4200+ | 2.2 GHz | 1 MB | Manchester | 89.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 4200+ | 2.2 GHz | 1 MB | Toledo | 89.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 4400+ | 2.2 GHz | 2 MB | Toledo | 110.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 4600+ | 2.4 GHz | 1 MB | Manchester | 110.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 4600+ | 2.4 GHz | 1 MB | Toledo | 110.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 4800+ | 2.4 GHz | 2 MB | Toledo | 110.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 FX-60 | 2.6 GHz | 2 MB | Toledo | 110.0 W | 90 nm |
Socket AM2
| Model | Clock | L2 Cache | Core | Power | Process |
| Athlon 64 X2 3600+ | 1.9 GHz | 1 MB | Brisbane | 65.0 W | 65 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 3600+ | 2.0 GHz | 512 KB | Windsor | 65.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 3800+ | 2.0 GHz | 1 MB | Windsor | 89.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 4000+ | 2.0 GHz | 2 MB | Windsor | 89.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 4000+ | 2.1 GHz | 1 MB | Brisbane | 65.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 4200+ | 2.2 GHz | 2 MB | Windsor | 89.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 4400+ | 2.2 GHz | 2 MB | Windsor | 89.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 4400+ | 2.3 GHz | 1 MB | Brisbane | 65.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 4600+ | 2.4 GHz | 1 MB | Windsor | 89.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 4800+ | 2.4 GHz | 2 MB | Windsor | 89.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 4800+ | 2.5 GHz | 1 MB | Brisbane | 65.0 W | 65 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 5000+ | 2.6 GHz | 1 MB | Windsor | 65.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 5000+ | 2.6 GHz | 1 MB | Windsor | 65.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 5000+ | 2.6 GHz | 1 MB | Brisbane | 65.0 W | 65 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 5200+ | 2.6 GHz | 2 MB | Windsor | 89.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 5400+ | 2.8 GHz | 1 MB | Windsor | 89.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 FX-62 | 2.8 GHz | 2 MB | Windsor | 125.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 5600+ | 2.8 GHz | 2 MB | Windsor | 89.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 X2 6000+ | 3.0 GHz | 2 MB | Windsor | 125.0 W | 90 nm |
Socket F
| Model | Clock | L2 Cache | Core | Power | Process |
| Athlon 64 FX-70 | 2.6 GHz | 2 MB | Windsor | 125.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 FX-72 | 2.8 GHz | 2 MB | Windsor | 125.0 W | 90 nm |
| Athlon 64 FX-74 | 3.0 GHz | 2 MB | Windsor | 125.0 W | 90 nm |
More Computer Architecture Articles:
• Change Raspberry Pi Default Configuration
• Electronic Circuits Basics
• Logical Versus Physical Memory Addresses
• The Fetch, Decode, Execute Cycle
• Microcontrollers
• The Android Operating System
• Computer Buses
• Factors in Choosing an Oscilloscope
• CPU Process Scheduling
• Operating System Memory Allocation Methods

