Most people think the microprocessor is the most important component of a computer, but much of a computer's performance is determined by the speed of its memory and by the type and speed of it peripheral ports.
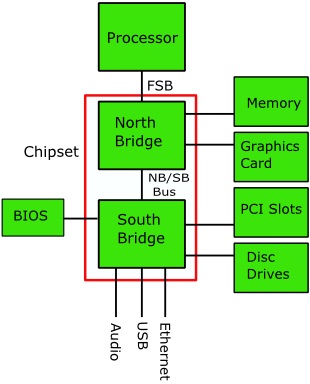
A computer's memory and peripheral ports connect through two highly integrated chips called simply the "chipset". The chipset consists of a northbridge chip and a southbridge chip.
The northbridge connects to the microprocessor through the Front-Side Bus (FSB). Through the northbridge the microprocessor is connected to the systems memory and the Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP).
The northbridge originally connected to the southbridge using the Peripheral Component Interconnect PCI) bus, but this created a bottleneck, so newer systems use a proprietary dedicated bus to connect to the northbridge to the southbridge.
The southbridge, sometimes called the I/O Controller Hub ICH) handles lower-speed features like the Basic Input/Output (BIOS) chip, an integrated audio controller, ATA and/or SATA (hard disk drive) controllers, and I/O ports like Ethernet, USB, and expansion slots like PCI and/or PCI Express bus.
The advantage of using a chipset is that microprocessors are already highly integrated, so to avoid stuffing more circuitry on the microprocessor chip, some of the computers functions can be off-loaded to the chip set. Another advantage is that these features can be operated with an independent clock, allowing the computer's owner to experiment with overclocking (replacing the oscillator crystal with a higher frequency crystal to try to increase performance).
However, beginning with AMD's Athlon 64-bit microprocessor and Intel's Core i series microprocessors, the memory controller has been removed from the northbridge chip and integrated into the microprocessor chip in order to increase performance. In today's modern computer's, the features of the chipset have been integrated into a single chip, like Intel's Z87 (but it's still referred to as the "chipset").
More Computer Architecture Articles:
• Computer Video Display
• Stored Program Architecture
• Operating System Services
• Factors in Choosing an Oscilloscope
• Operating System Process Control Block
• Binary Floating-Point Numbers
• CPU Chip Packaging
• Round-Robin CPU Scheduling Algorithm
• Program Flow Charting
• Basic Computer Architecture

